README.md
7 Segment display
- But du projet
- I/O utilisées
- Explication de l'algorithme
- Résultats
L'ensemble des codes, images et vidéos sont compris dans ce répertoire.
But du projet
Nous avons eu comme projet d'afficher différentes choses sur un écran en passant par son port VGA.
I/O utilisées
Tout d'abord, voyons les entrées/sortie que nous avons utilisées.
entity vga_controller is
Port (clk_fpga : in std_logic;
sw : in std_logic_vector(15 downto 0);
vgaRed : out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
vgaGreen : out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
vgaBlue : out std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
Hsync : out std_logic;
Vsync : out std_logic);
end vga_controller;
- clk_fpga : le signal de clock du fpga
- sw : interrupteurs pour commander les couleurs
- vgaRed/Green/Blue : permet de commander la couleur à afficher
- Hsyn : synchronisation horizontale
- Vsyn : synchronisation verticale
Dans le fichier de contrainte :
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN V17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[0]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN V16 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[1]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W16 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[2]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[3]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W15 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[4]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN V15 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[5]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W14 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[6]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W13 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[7]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN V2 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[8]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN T3 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[9]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN T2 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[10]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN R3 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[11]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN W2 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[12]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN U1 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[13]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN T1 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[14]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN R2 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {sw[14]}]
Cela permet associer les interrupteurs au tableau sw. Dans le fichier de contrainte :
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN G19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaRed[0]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN H19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaRed[1]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN J19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaRed[2]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN N19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaRed[3]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN N18 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaBlue[0]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN L18 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaBlue[1]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN K18 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaBlue[2]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN J18 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaBlue[3]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN J17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaGreen[0]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN H17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaGreen[1]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN G17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaGreen[2]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN D17 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports {vgaGreen[3]}]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN P19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports Hsync]
set_property -dict { PACKAGE_PIN R19 IOSTANDARD LVCMOS33 } [get_ports Vsync]
On associe tout les pins du connecteur VGA avec nos signaux
Explication de l'algorithme
Pour que le code soit compréhensible facilement, nous avons crée plusieurs process pour les différentes utilités.
Les signaux
signal clk_65MHz : std_logic;
signal Hcount : integer range 1344 downto 1 := 1;
signal Vcount : integer range 1083264 downto 1 := 1;
signal myRed: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
signal myBlue: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
signal myGreen: std_logic_vector(3 downto 0);
signal leftLimit: integer range 1025 downto 0:= 0;
signal rightLimit: integer range 1025 downto 0:= 100;
signal upLimit: integer range 768 downto 0:= 0;
signal downLimit: integer range 768 downto 0:= 100;
signal pixelX: integer range 1344 downto 1:= 1;
signal pixelY: integer range 768 downto 1;
- *Limit : Permet de délimiter les coordonnées du carré
- pixel* : Désigne la coordonnée du pixel que nous affichons ### Les process #### 1er process
process(clk_65MHz)
begin
if clk_65MHz'event and clk_65MHz = '1' then
-- Gestion du vga
-- Syncro horizontale
if Hcount < 1025 then
-- affichage
Hsync <= '1';
Hcount <= Hcount + 1;
elsif Hcount < 1049 then
-- Fp
Hsync <= '1';
Hcount <= Hcount + 1;
elsif Hcount < 1185 then
-- Pw
Hsync <= '0';
Hcount <= Hcount + 1;
elsif Hcount < 1344 then
-- Bp
Hsync <= '1';
Hcount <= Hcount + 1;
else
Hcount <= 1;
end if;
-- Synchro vertical
if Vcount < 1032193 then
-- Affichage de toutes les lignes
Vsync <= '1';
Vcount <= Vcount + 1;
elsif Vcount < (1032193 + 4032) then
--Fp
Vsync <= '1';
Vcount <= Vcount + 1;
elsif Vcount < (1032193 + 4032 + 8064) then
--Pw
Vsync <= '0';
Vcount <= Vcount + 1;
elsif Vcount < (1032192 + 4032 + 8064 + 38976) then
--Bp
Vsync <= '1';
Vcount <= Vcount + 1;
else
Vcount <= 1;
end if;
end if;
end process;
Ce process permet de suivre les différents signaux de synchronisation verticale et horizontale grâce à une horologe 65MHz.
2eme process
process(clk_65MHz)
-- Gestion de l'affichage
begin
if clk_65MHz'event and clk_65MHz = '1' then
if pixelX > leftLimit and pixelX < rightLimit and pixelY > upLimit and pixelY < downLimit then
-- Carré
vgaRed <= myRed;
vgaBlue <= myBlue;
vgaGreen <= myGreen;
elsif Hcount < 1025 and pixelY < 769 then
-- Background
vgaRed <= (others => '1');
vgaBlue <= (others => '1');
vgaGreen <= (others => '1');
else
-- Hors pixel
vgaRed <= (others => '0');
vgaBlue <= (others => '0');
vgaGreen <= (others => '0');
end if;
end if;
end process;
Ce process prends en charge l'affichage du fond de l'écran et ainsi que l'affichage du carré.
3eme process
process(clk_65MHz)
begin
if clk_65MHz'event and clk_65MHz = '1' then
if Vcount = 1032193 then
if rightLimit > 1024 and downLimit > 768 then
leftLimit <= 0;
rightLimit <= 100;
upLimit <= 0;
downLimit <= 100;
elsif rightLimit > 1024 then
leftLimit <= 0;
rightLimit <= 100;
upLimit <= upLimit + 1;
downLimit <= downLimit + 1;
else
leftLimit <= leftLimit + 1;
rightLimit <= rightLimit +1;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
Ce process permet de gerer le mouvement de notre carré grâce à ces coordonnées.
4eme process
process(clk_65MHz)
-- Simplification des valeurs d'écran
begin
if clk_65MHz'event and clk_65MHz = '1' then
if Vcount = 1 then
pixelY <= 1;
elsif Hcount = 1025 then
pixelY <= pixelY + 1;
end if;
end if;
end process;
Résultats
-Nous avons dans un premier temps réussi à afficher un écran dont la couleur est commandée par 12 interrupteurs (4 interrupteurs par couleurs)

-Puis nous avons reussi à afficher un carré dans un coin de l'écran (toujours commandé en couleurs par les interrupteurs)
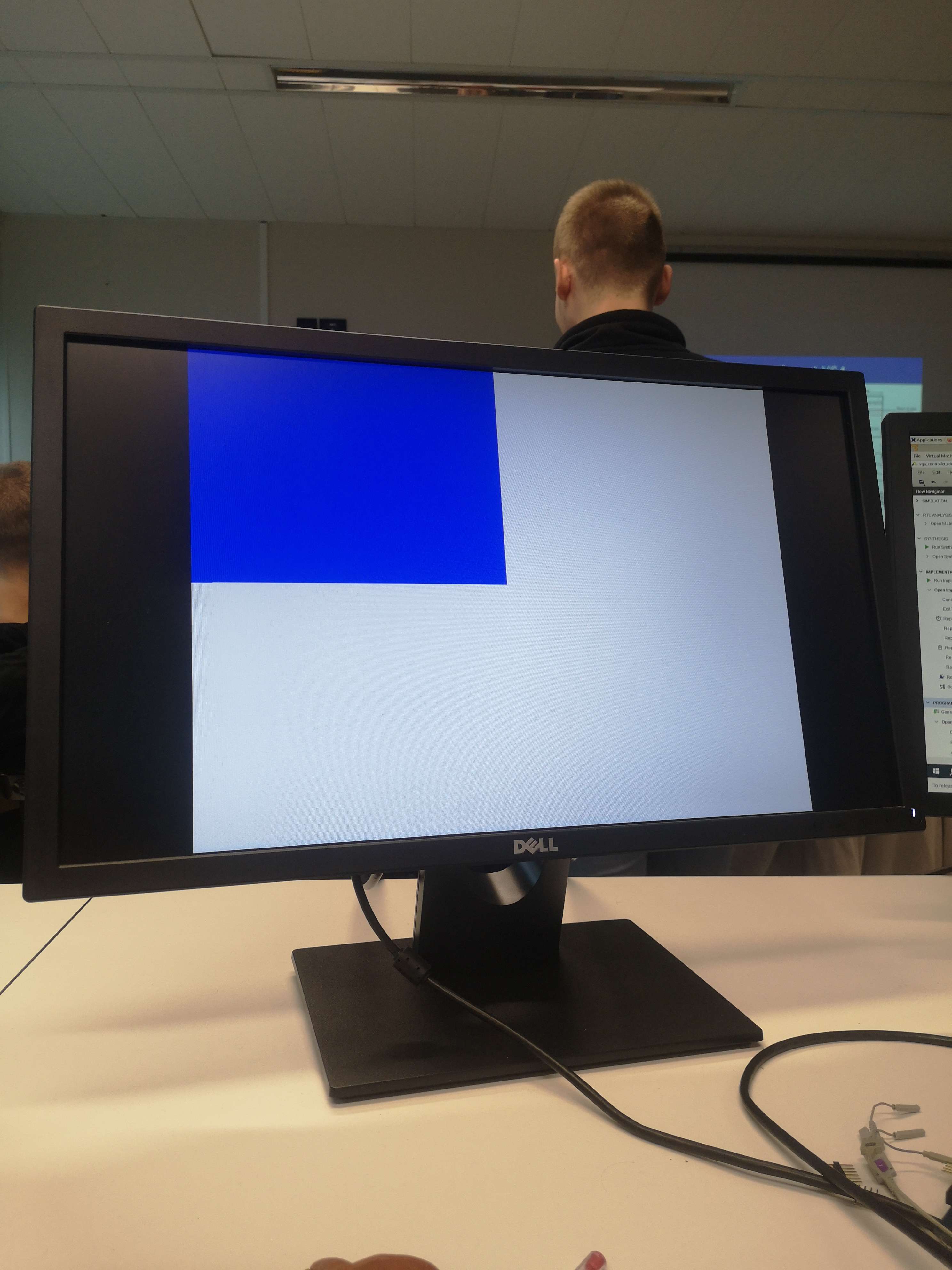
-Finalement avec la separation du code en process et en ajoutant des fonctionnalités, nous avons réussi à animer le carré qui se déplace de droite à gauche et revient à gauche dès qu'il touche le coin droit tout en descendant.
